The dollar rate in India is rising in 2025 due to a mix of global and domestic pressures, mostly from high oil prices and strong US economic data to shifting capital flows and Reserve Bank interventions.
Here’s a clear look at why USD to INR is increasing and what it means for the Indian economy.
How the US Dollar Works in India’s Economy
To understand why the dollar rate is increasing in India, it helps to first know how the US dollar functions in the Indian financial system.
The US dollar is the primary currency used for global trade and cross-border settlements, including India’s key imports such as oil, machinery, and electronics. Whenever Indian companies buy goods from abroad, they must pay in USD, creating constant demand for the dollar.
Because the dollar is central to these transactions, any rise in USD demand, whether for trade, debt payments, or capital outflows, directly affects the rupee’s value.
That’s why shifts in global trade patterns or US monetary policy often ripple through India’s forex market.
Why is USD to INR Increasing?
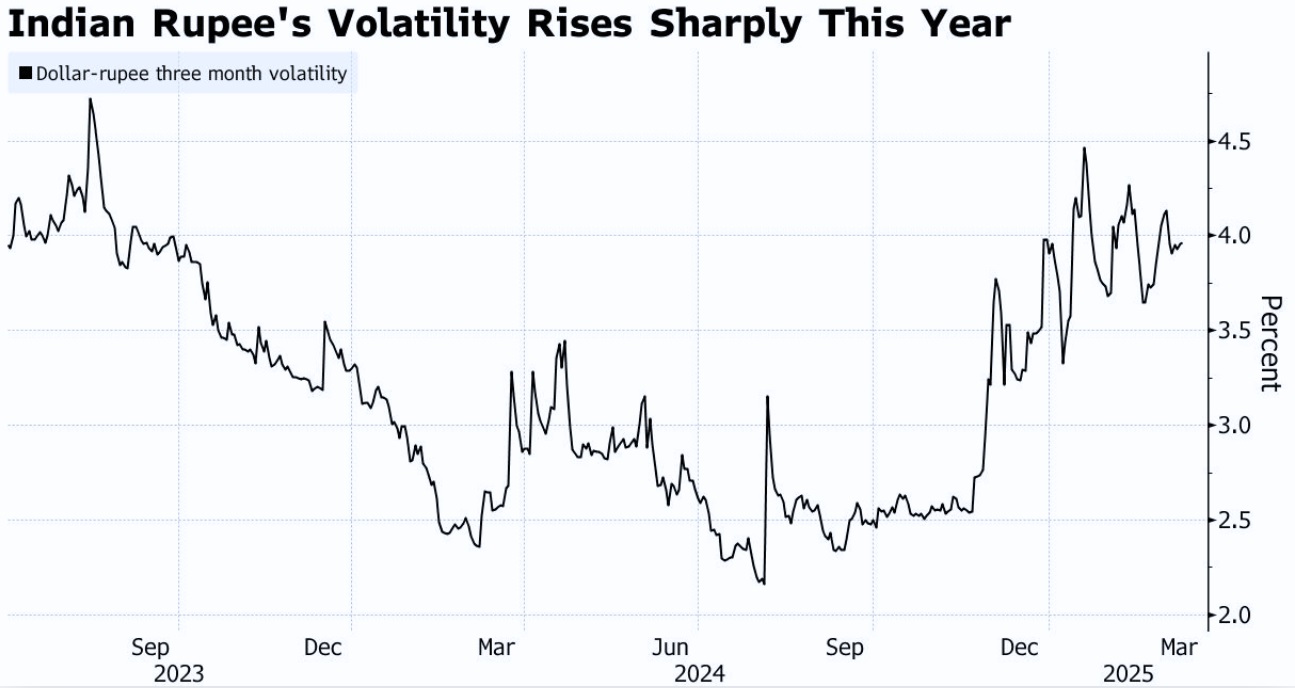
The USD to INR rate has been climbing steadily in 2025, with the rupee hovering near record lows.

This increase is driven by stronger US fundamentals, a firm US Dollar Index (DXY), and growing global risk aversion.
When the US Federal Reserve signals higher-for-longer interest rates, international investors often move funds into dollar-based assets, strengthening the USD while weakening emerging-market currencies like the Indian rupee.
This causes a higher USD-INR exchange rate, reflecting not only currency demand but also global capital reallocation.
1.Global Oil Prices and Geopolitical Influence
One of the strongest reasons why the dollar rate is increasing in India is the cost of crude oil.
India imports more than 80% of its oil, and these transactions are settled in US dollars. When global oil prices rise for instance, from $75 to $90 per barrel, Indian importers must buy more dollars to cover energy costs. This increases demand for USD, putting downward pressure on the rupee.
Events such as Middle East tensions or OPEC+ supply cuts often cause these price spikes. Even short-term disruptions can lead to rupee weakness unless the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) intervenes to stabilize the market.
Simply put, higher oil prices mean higher dollar demand, which is one of the clearest explanations for why USD to INR is increasing in 2025.
2.Corporate Dollar Hedging and Importer Demand
Large Indian corporations also contribute to the rising dollar price in India through hedging activity.
Companies with foreign loans or import contracts often purchase dollars in advance to manage exchange-rate risk. When businesses expect the rupee to weaken, they accelerate these hedging purchases, boosting dollar demand in domestic forex markets.
Conversely, exporters, particularly IT and pharmaceutical firms that earn in dollars may hedge receivables, adding supply to the market. However, when import-driven hedging outweighs export flows, the USD-INR tends to rise.
3.Foreign Capital Flows and RBI Intervention
Foreign institutional investors (FIIs) play a critical role in shaping the USD-INR trend. When FIIs invest in Indian equities and bonds, they convert USD into INR, supporting the rupee. But when they pull money out, often during global risk-off phases or when US yields rise, the process reverses. Funds flow back to the US, increasing demand for the dollar and weakening the rupee.
The RBI frequently steps in to curb excessive volatility by buying or selling dollars from its forex reserves. In 2025, it has actively intervened whenever the rupee weakens beyond ₹86.50 per USD, using its reserves to maintain orderly market conditions.
This intervention is vital, but it also shows the pressure the rupee faces one more reason why the dollar rate is increasing in India this year.
4.US Federal Reserve Policy and Global Dollar Strength
Another major factor behind why USD to INR is increasing is the US Federal Reserve’s monetary policy. When the Fed raises interest rates, the US Dollar Index (DXY) typically strengthens because global investors seek higher returns in US assets. This leads to capital outflows from emerging markets like India, where yields are relatively lower, and causes the rupee to depreciate.
If the RBI does not match these rate hikes, the yield gap widens further, encouraging more outflows and increasing USD-INR pressure.
In 2025, the Fed’s hawkish stance and strong US economic data have contributed directly to why the dollar rate is rising in India, as global investors rebalance portfolios toward the United States.
5.Domestic Economic Indicators and Structural Pressures
India’s internal fundamentals also explain why the rupee is weakening against the dollar.
Key factors include:
Inflation: Persistent domestic inflation reduces rupee value and investor confidence.
Trade Deficit: A widening deficit means more dollars are leaving the country to pay for imports.
Forex Reserves: RBI reserves above $600 billion provide a buffer, but heavy intervention can deplete them over time.
Economic Growth & Policy Stability: Strong GDP growth and fiscal discipline attract investment, while uncertainty or slow reforms can trigger capital flight.
In 2025, higher energy imports and moderate inflation have slightly widened India’s trade deficit, though robust services exports and foreign direct investment (FDI) have helped soften the impact.
Why the Dollar Rate Is Increasing in India (2025 Summary)
In 2025, the steady increase in the dollar rate in India can be summarized to several overlapping trends:
Rising global oil prices and higher import bills
A stronger US dollar backed by elevated US interest rates
Capital outflows from Indian markets toward safer US assets
Increased corporate hedging demand for USD
Limited RBI intervention flexibility amid reserve management
Together, these factors create sustained pressure on the rupee, pushing the USD-INR pair to new highs.
Why Dollar Rate (USD) Increase in India Matters for Investors
For investors and traders, the rising dollar rate affects investment returns, import costs, and inflation.
A stronger USD raises prices for imported goods, fuels inflation, and influences decisions on foreign portfolio allocations. For exporters, however, a weaker rupee can boost competitiveness by increasing the value of overseas earnings.
Monitoring why the dollar rate is increasing in India helps investors adjust hedging strategies, manage currency exposure, and identify opportunities in global markets.
Future Outlook: What’s Ahead for the Indian Rupee (INR)

Going into late 2025 and beyond, analysts expect the Indian Rupee (INR) to remain range-bound but fundamentally stable, anchored by strong domestic growth and proactive policy management.
RBI Support: The Reserve Bank of India is likely to continue intervening strategically to smooth volatility and prevent sharp depreciation, keeping USD/INR within a controlled range.
Growth Momentum: With GDP growth forecast near 6.5%, India’s economic fundamentals remain among the strongest in emerging markets.
Export Tailwinds: Expanding services exports and steady FDI inflows could provide medium-term support to the rupee.
Global Headwinds: Persistent global monetary tightening, a stronger US dollar, or renewed oil price shocks could cap any major rupee gains.
Economists from major institutions such as Nomura and ICICI Securities anticipate USD/INR to trade between 83.00 and 84.50 by end-2025, with a mild strengthening trend into 2026.
Some international banks forecast the rupee could appreciate toward 82.00 levels if inflation remains near the RBI’s 4% target and oil prices stay below $85/barrel.
Conversely, if the Federal Reserve delays rate cuts or risk sentiment weakens, USD/INR could test 85.50 –86.00 in early 2026 before stabilizing.
Overall, economists see limited downside risk for the rupee and a modest appreciation bias in 2026, provided inflation stays near target and fiscal discipline continues.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1.Why is the dollar rate increasing in India in 2025?
The dollar rate in India is rising due to higher global oil prices, strong U.S. economic performance, and continued capital outflows from emerging markets. The U.S. Federal Reserve’s high interest rate policy has also boosted dollar demand, making the rupee weaker against the USD.
2.How does the U.S. dollar affect India’s economy?
The U.S. dollar plays a vital role in India’s financial system because most of India’s international trade, including oil, machinery, and technology imports, is settled in USD. When the dollar strengthens globally, India needs to spend more rupees to buy the same amount of goods, increasing import costs and inflation.
3.Will the Indian Rupee keep weakening against the USD?
Analysts expect the rupee to stay within a controlled range in 2025, supported by India’s strong GDP growth and RBI intervention. However, persistent global risks such as high oil prices and U.S. rate hikes could keep the USD-INR exchange rate elevated.
4.Is a higher USD to INR rate bad for India?
Not always. While a weaker rupee increases import costs and inflation, it also boosts export competitiveness by making Indian goods and services cheaper abroad. The impact depends on India’s trade balance, inflation control, and policy response.
Final Thoughts
The rising dollar rate in India reflects a complex mix of global forces and domestic fundamentals, not just short-term speculation.
From oil and geopolitics to interest rates and capital flows, every factor plays a role in determining how the rupee moves against the US dollar.
In 2025, these pressures have aligned to keep USD-INR near historic highs. While the RBI continues to balance the market, the long-term path of the rupee will depend on energy prices, inflation control, and foreign investment stability.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.

























