The SPY ETF, officially known as the SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust, is one of the most well-known and widely traded exchange-traded funds in the world. For investors seeking broad exposure to the U.S. equity market, SPY represents a powerful and accessible tool. Whether you're a novice investor looking for diversification or a seasoned trader seeking liquidity, understanding how the SPY ETF works is essential.
What is SPY? History & Overview
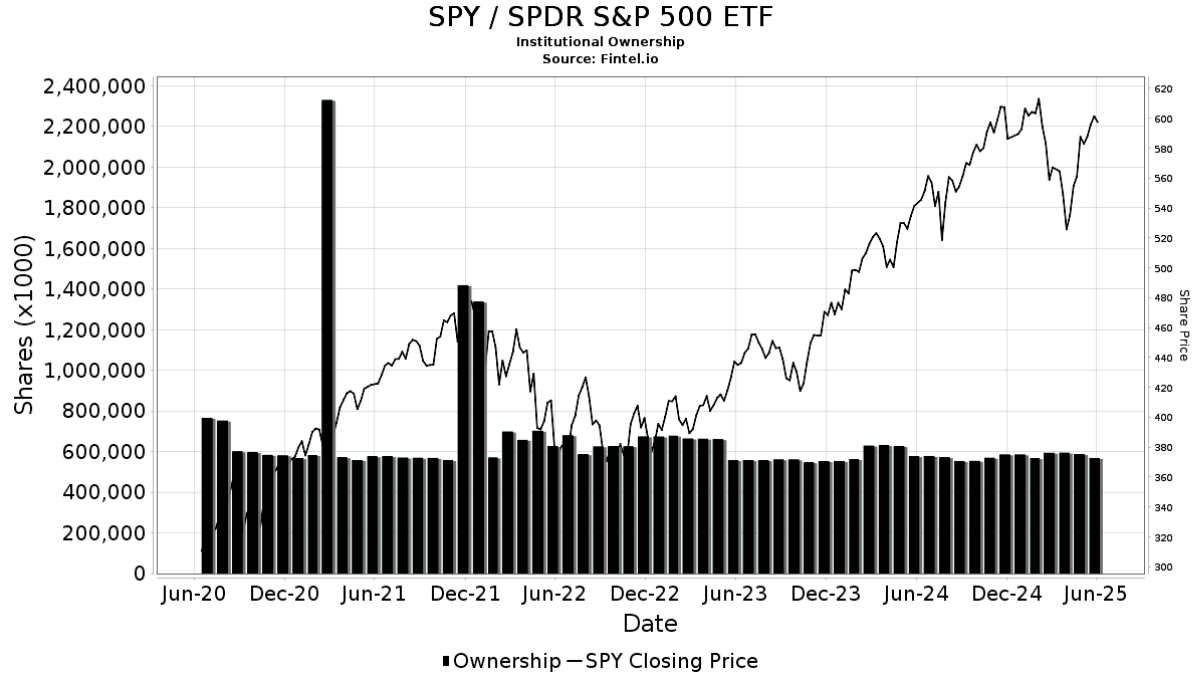 Launched on 22 January 1993 by State Street Global Advisors, SPY was the first U.S.-listed exchange-traded fund (ETF) and remains one of the largest by assets under management. It was designed to track the performance of the S&P 500 Index, an index that represents 500 of the largest publicly traded companies in the United States, covering approximately 80% of the available market capitalisation.
Launched on 22 January 1993 by State Street Global Advisors, SPY was the first U.S.-listed exchange-traded fund (ETF) and remains one of the largest by assets under management. It was designed to track the performance of the S&P 500 Index, an index that represents 500 of the largest publicly traded companies in the United States, covering approximately 80% of the available market capitalisation.
The ETF trades on the NYSE Arca exchange under the ticker symbol SPY and has become synonymous with low-cost, broad-based equity exposure. Its innovation helped popularise passive investing, giving ordinary investors access to institutional-quality portfolio tools.
How SPY Tracks the S&P 500 Index
SPY uses a full replication strategy, meaning it holds all 500 constituents of the S&P 500 Index in the same proportion as the index itself. This allows it to mirror the performance of the S&P 500 with high accuracy.
The S&P 500 is a market-capitalisation-weighted index, which means companies with larger market values (like Apple, Microsoft, and Nvidia) make up a larger portion of the index—and therefore, a larger portion of SPY's holdings. This gives SPY investors immediate exposure to leading sectors such as technology, healthcare, financials, and consumer discretionary.
The ETF is rebalanced quarterly in line with index updates, and any dividends paid by underlying companies are passed through to SPY shareholders via quarterly distributions.
Liquidity & Trading Volume
One of SPY's most compelling features is its exceptional liquidity. On an average day, SPY trades tens of millions of shares, making it one of the most actively traded securities in the world. This high trading volume leads to tight bid-ask spreads, which is advantageous for both long-term investors and short-term traders.
Its deep liquidity means investors can enter and exit positions with minimal slippage, even when trading in large quantities. For institutions, hedge funds, and retail traders alike, SPY's liquidity reduces friction and enables highly flexible trading strategies.
Expense Ratio & Costs
SPY offers relatively low-cost exposure to the entire U.S. large-cap equity market. Its annual expense ratio is 0.09%, which means investors pay just $9 per year for every $10.000 invested.
While SPY is cost-effective, it's worth noting that other S&P 500-tracking ETFs—such as Vanguard's VOO or iShares'IVV—offer even lower expense ratios (0.03%). However, SPY remains popular due to its unparalleled liquidity and long track record.
Beyond the expense ratio, SPY investors should also be aware of trading costs such as brokerage commissions (if any) and bid-ask spreads, though these tend to be minimal due to the ETF's volume and popularity.
Tax & Structural Considerations
SPY is structured as a Unit Investment Trust (UIT), which differentiates it from other ETFs that are organised as open-end funds. This UIT structure imposes a few limitations:
SPY cannot reinvest dividends; instead, it holds them in cash until distributed.
It cannot lend out securities, which limits potential income from securities lending compared to other ETFs.
While these restrictions may slightly reduce SPY's total return compared to peers like IVV or VOO, the impact is usually minimal for long-term investors. However, the structure can result in slightly less efficient tax treatment, particularly for investors in taxable accounts.
Conclusion: Is SPY ETF Right for You?
The SPY ETF remains a cornerstone in the world of passive investing, combining broad market exposure, high liquidity, and a long-standing track record. For those seeking a simple and effective way to invest in the U.S. stock market, SPY offers a reliable and accessible option.
While it may not have the lowest fees compared to its rivals, SPY's incredible trading volume and ease of access make it a standout choice for both individual investors and institutions. By understanding the fundamentals of the SPY ETF—how it's structured, how it tracks the S&P 500. and the costs involved—investors can make more informed decisions and build a robust foundation for long-term wealth creation.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.



 Launched on 22 January 1993 by State Street Global Advisors, SPY was the first U.S.-listed exchange-traded fund (ETF) and remains one of the largest by assets under management. It was designed to track the performance of the S&P 500 Index, an index that represents 500 of the largest publicly traded companies in the United States, covering approximately 80% of the available market capitalisation.
Launched on 22 January 1993 by State Street Global Advisors, SPY was the first U.S.-listed exchange-traded fund (ETF) and remains one of the largest by assets under management. It was designed to track the performance of the S&P 500 Index, an index that represents 500 of the largest publicly traded companies in the United States, covering approximately 80% of the available market capitalisation.


















