Understanding the natural rate of unemployment is key to making sense of how labour markets function over time. Unlike cyclical unemployment that rises and falls with economic booms and recessions, the natural rate of unemployment reflects a baseline level that persists even in healthy economies.
In this article, we unpack the natural rate of unemployment through seven essential insights that explain what it is, what causes it, and why it matters for policymakers, businesses, and investors alike.
Natural Rate of Unemployment: 7 Things to Know
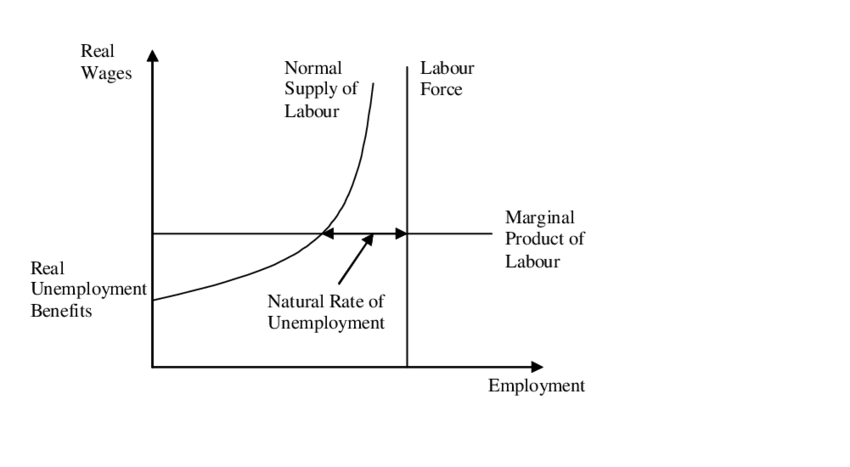
1. The Natural Rate of Unemployment Is Always Present
Even when an economy is performing at its full potential, some level of unemployment is expected. This baseline is called the natural rate of unemployment. It includes workers who are transitioning between jobs and those whose skills no longer match the needs of the market.
The existence of this rate means that zero unemployment is neither realistic nor desirable, as it could indicate a rigid and inefficient labour market.
2. Frictional and Structural Factors Are the Main Drivers
The natural rate of unemployment is made up primarily of two types of joblessness: frictional and structural. Frictional unemployment occurs when people voluntarily leave jobs or enter the workforce, taking time to find suitable roles.
Structural unemployment arises when there is a mismatch between workers' skills and the jobs available, often due to technological change, globalisation or shifts in demand. Both of these are natural and ongoing processes in any dynamic economy.
3. It Varies Over Time and Between Countries
There is no fixed percentage that applies universally to the natural rate of unemployment. It can change over time within a country and vary significantly between nations. In many developed economies, it is often estimated at around 4 to 5 percent.
However, changes in labour market regulations, demographic shifts, technological developments and education systems can cause the natural rate to rise or fall.
4. The Natural Rate of Unemployment and Full Employment Can Coexist
Contrary to popular belief, full employment does not mean zero unemployment. Economists often define full employment as the point at which only the natural rate of unemployment exists.
At this level, everyone who wants a job at the current wage rate and has suitable skills is employed. Any remaining unemployment is either frictional or structural. Full employment is therefore compatible with a certain level of ongoing unemployment in the economy.
5. The Natural Rate Is Not Directly Observable
Unlike actual unemployment figures that can be measured, the natural rate of unemployment must be estimated using economic models. These models rely on long-term data and assumptions about inflation, productivity and labour market behaviour.
This makes it a theoretical concept rather than a concrete figure, though it remains extremely useful for shaping policy and analysing trends.
6. Why Policymakers Monitor It Closely
Policymakers, especially central banks, watch the natural rate of unemployment closely when designing interest rate strategies and fiscal policies. If actual unemployment drops well below the natural rate, it may indicate an overheated economy and rising inflation.
Conversely, if unemployment is above the natural rate for extended periods, it can signal underperformance and the need for stimulus. Understanding where the economy stands in relation to the natural rate helps guide stable and sustainable decision-making.
7. Key Features of the Natural Rate of Unemployment
Here are some defining characteristics that distinguish the natural rate of unemployment:
1) It does not result from economic downturns.
2) It reflects long-term equilibrium.
3) It can shift based on policy and innovation.
4) It coexists with inflation stability.
5) It informs the non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment (NAIRU).
Conclusion
The natural rate of unemployment remains one of the most important yet often misunderstood concepts in labour economics. It captures the idea that some unemployment is a normal, even healthy, feature of a well-functioning economy.
By understanding what drives the natural rate, how it evolves, and why it matters, we gain clearer insight into the broader economic picture.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.























